|
|
| Role |
OS Version |
Description / Resolution |
Microsoft KB Ref. etc. |
| DNS |
Windows
Server
2008 / R2 |
Frequent occasions when DNS could not resolve
queries for host names in some
TLDs , including .co.uk.
A dnscmd /ClearCache or a DNS
service restart would clear the problem - but it
would soon reoccur. |
Microsoft Knowledge
Base http://support.microsoft.com/kb/968372/en-us
Technet References
Understanding
Forwarders
DNS Forwarders vs Root Hints
Configure a DNS Server to Use
Forwarders
OpenDNS IP Addresses
208.67.222.222
208.67.220.220 |
| Resolution |
This is a known issue in Server 2008 & 2008R2
when the DNS server is using root hints to provide
the IP addresses of
root name servers. This problem does not occur
if the DNS server is set to use forwarders, rather
than root hints, for internet name resolution. I
configured my DNS servers to use forwarders and
pointed to the Open DNS servers. |
| All |
Windows
Server
2008 / R2 |
Could not ping my servers from
inside the domain |
Various Google hits, including :-
Why can't I ping my server? |
| Resolution |
By default, the Windows firewall blocks ping
requests, the easiest way to enable it is from the
Windows Firewall applet in the Control Panel.
Select the Inbound Rules
tree option, scroll down to
File and
Printer Sharing (Echo Request . . )
and enable the appropriate rule(s). There are
separate rules for IPv4 and IPv6 and for Private and
Domain networks. |
 |
| RDP |
Windows Server 2003 |
Could not RDP to Windows Server
after reboot |
Various Google hits, including
:-
Remote Desktop does not connect after a restart
|
| Resolution |
In summary, I had to
1.) Stop
the IPSec service on the remote machine, and set its
startup mode to "Manual"
2.) Restart the remote
machine
3.) Restart the IPSec service and set
its startup mode back to "Automatic".
This can
ALL be done remotely, even without RDP |
I was able to stop the service
remotely, but could not restart the server using the
instructions
Instead, I used Shutdown.exe as
described in
How to Shut Down and Reboot Remote PCs via the
Command Prompt or
Restart or Shut Down a Windows Remote Computer and
Document the Event |
| All |
Windows
Server
2008 / R2 |
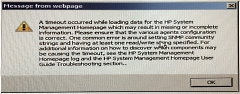
After replacing a failed system
board in one of my DL360G4p servers, the HP System
Management Homepage application did not open. After
an extended time, a dialogue box advised that "a
timeout occurred while loading data for the HP
System Management Homepage which may results in
missing or incomplete information". The message box
suggested that the SNMP configuration may have been
to blame, but as this configuration had not changed,
it didn't seem likely.
It turned out that the
older system BIOS on the replacement system board
was the cause of the problem. Upgrading the BIOS
cured it. |
 |
| AD |
Windows
Server
2008 / R2 |
One of my domain controllers
shutdown due to a faulty CPU fan tray and went
through cycles of powering up and down as the
temperature cooled and heated. To fix the fault, I
had the server out of the rack and decided that I
wanted to boot it up to try it when it was not
connected to the domain. This was a pretty big
mistake !
When the machine started, there was
a Message Box (which I didn't read properly - duh!)
about Windows reconfiguring something - but the
system appeared to start OK, so I put it back in the
rack and powered it on.
Unfortunately, I also
missed that the CMOS battery had died and the
machine stated up with an ancient date & time
setting so would not connect to the domain. When I
changed the CMOS battery and corrected the date &
time, the server appeared to connect to the domain
OK, but Windows asked to be reactivated - which I
did.
I then started to see Event ID 2092 in
the Event Log, with the accompanying message
"This server is the owner of the following FSMO
role, but does not consider it valid. For the
partition which contains the FSMO, this server has
not replicated successfully with any of its partners
since this server has been restarted. Replication
errors are preventing validation of this role . . .
. . . ."
The repadmin /showrepl command confirmed
that at this point, replication between the domain
controllers was no longer working.
|
I fixed it, but I didn't write down
how - ooops! |
| |
|
|
|
| All |
Windows
Server
2008 / R2 |
When trying to apply some Windows
Updates, a couple of the updates failed with error
code 0x80092004 |
It turns out that this issue was
caused in 2019 by Microsoft changing the security
signing of updates from
SHA-1
to
SHA-2. Without the application of a previous KB,
Windows Update was looking for SHA-1 signed updates
and rejecting those signed with the newer SHA-2. |
| Resolution |
For Windows Server 2008-R2, the
missing updates were
KB4474419 and
B4490628.
I downloaded them directly from
the Microsoft Update Catalog
here and
here |
If you download and install updates
automatically, it is likely that you won't see this
issue. I prefer to download and apply updates under
my control, so this critical update wasn't applied
until I downloaded it from the Windows Update site
and applied it manually. |
| n/a |
Windows Server 2016 |
When trying to map a network share
for a new tape backup job, I was unable to add the
share with Windows telling me that :-
"No
more connections can be made to this remote computer
at this time because there are already as many
connections as the computer can accept" |
I don't know whether I had made a
mistake with installation and licensing of the
server, but I was able to get around it by making a
Registry change as described on
techsalsa.com
here
This changes the number of
concurrent SMB connections from its default of 10 to
a maximum of 255
|
| Resolution |
Using
Regedit, locate the key :
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Lanmanserver\Parameters
Create a new DWORD Value called
MaxMpxCt
Set its value to the
number of connections allowed - I chose 100 |
| n/a |
Windows Server 2016/19 |
Microsoft's "new" Edge browser is not included with
Server 2016/2019 which still rely on Internet
Explorer and Edge downloads are not available. The
version of IE installed does have some enhanced
security features, which, amongst other things,
makes the download and installation of other
browsers a bit of a pain. All connections to the
internet are blocked by default in IE, making its
use a pain!
So, how could I install Chrome on
Server 2016/2019 without jumping through too many
hoops? |
| Resolution |
Solution : execute the PowerShell script below, by
pasting it into PowerShell window
See
snel.com for details
| $LocalTempDir = $env:TEMP; $ChromeInstaller
= "ChromeInstaller.exe"; (new-object
System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile('http://dl.google.com/chrome/install/375.126/chrome_installer.exe',
"$LocalTempDir\$ChromeInstaller"); & "$LocalTempDir\$ChromeInstaller"
/silent /install; $Process2Monitor = "ChromeInstaller";
Do { $ProcessesFound = Get-Process |
?{$Process2Monitor -contains $_.Name} |
Select-Object -ExpandProperty Name; If ($ProcessesFound)
{ "Still running: $($ProcessesFound -join ',
')" | Write-Host; Start-Sleep -Seconds 2 }
else { rm "$LocalTempDir\$ChromeInstaller" -ErrorAction
SilentlyContinue -Verbose } } Until (!$ProcessesFound)
|
|
| n/a |
Windows Server 2016/19 |
Bloated Windows Server Updates
I installed
the Evaluation versions of Windows Server 2016 and
2019 with what I thought was a reasonable amount of
disk space configured. I allocated 40GB, 8 GB more
than the minimum specified by Microsoft for the
system partition. These machines were going to have
minimal additional software installed, so I expected
that 40 GB would last for a while. After
installation, about 10GB was taken up by the OS,
however, after updating, the disk usage pretty much
doubled! WTF ??
The Windows\Winsxs
subdirectory is used to store files needed for
system recovery, including rolling back updates (see
a longer description
here or
here). The files in there shouldn't be deleted
manually, but if you are happy to purge outdated
updates etc., you can use the
Deployment Image Servicing and Management
(DISM) tool, with the options shown below, to remove
all superseded versions of every component in the
Windows component store.
From an elevated
command prompt, enter
Dism.exe /online /Cleanup-Image /StartComponentCleanup
/ResetBase
Note: I
**think** that Windows Server is supposed to
automatically purge at least some of the outdated
Windows updates, but I didn't want to wait until
Windows decided it was time and wanted a way to
recover the wasted disk space when I wanted to. |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|